Virology Testing
Your antimicrobial products need proven virucidal efficacy data for regulatory approval and market differentiation. Element's comprehensive GLP/cGMP virology testing delivers defensible results for global regulatory submissions—with expert guidance, accelerated timelines, and custom protocols tailored to your specific products. Our 30+ years of experience and regulatory defense support successful product registrations.
What is Virology Testing at Element?
Virology testing evaluates how effectively products reduce, destroy, or inactivate viruses on surfaces, in materials, or in suspension. At Element, we provide complete virucidal efficacy testing services for antimicrobial products, pharmaceuticals, disinfectants, sanitizers, and treated articles. Our GLP and cGMP-compliant laboratories test against a wide array of BSL2 and BSL3 human and veterinary viruses, including SARS-CoV-2 variants, with specialized expertise in testing emerging viral threats, to support your product claims and regulatory submissions worldwide.

What Can Element Offer You For Virology Testing?
Key Tests Offered
Key Tests Offered
Your regulatory submissions demand comprehensive testing services tailored to your specific product claims. Element's complete virucidal testing portfolio supports your entire product development journey from initial screening to final submission. Our industry-leading virologists deliver testing for standard and specialized claims, including virucidal efficacy for direct-contact disinfection, residual protection, treated articles, and more.
- GLP virucidal efficacy testing for regulatory submissions
- Residual virucidal efficacy testing for long-lasting claims
- Treated article virucidal testing (fabrics, surfaces)
- Disinfectant and sanitizer virucidal testing
- EN virucidal testing for European regulatory compliance
- cGMP virology testing for pharmaceutical products
- Custom protocol development for unique applications
Products We Test
Products We Test
Your antimicrobial products require different testing approaches based on their formulation and application method. We test liquid disinfectants, aerosol sprays, pre-saturated towelettes, treated fabrics and surfaces, residual/long-lasting antimicrobial products, and pharmaceutical products. Our testing capabilities extend across household, hospital, and veterinary applications, ensuring your product efficacy data meets the specific requirements for your intended market.
- Hard surface disinfectants (liquids, sprays, wipes)
- Soft surface antimicrobials (fabric treatments, laundry additives)
- Long-lasting residual products (coatings, treated surfaces)
- Copper-containing antimicrobial surfaces
- Antimicrobial pesticide devices
Methods And Solutions Offered
Methods And Solutions Offered
Your product's unique formulation and application require specialized testing methodologies tailored to its specific characteristics. We offer comprehensive testing approaches including suspension-based methods, hard and soft surface evaluations, residual efficacy with wear simulation, surrogate virus testing, and specialized techniques for pharmaceuticals. Our methods support both standard and custom testing protocols across all major regulatory frameworks. Additionally, we provide specialized methodologies for assessing the degree of homogeneity and distribution of virucidal active ingredients, and testing for viral contamination in cell cultures and cell banks compliant with 21 CFR Part 58.
- Suspension-based testing (ASTM E1052, BS EN 14476, BS EN 14675)
- Hard surface testing (ASTM E1053, BS EN 16777)
- Soft surface testing (fabric, laundry additive)
- Residual efficacy testing with wear simulation
- Surrogate virus testing for difficult pathogens
- Topical skin products using ex-vivo models
- Disinfection validation/qualification (USP 1072)
- Custom protocol development for specialized applications
Regulatory expertise advantage
Your products face complex regulatory hurdles that vary across global markets. Our consultative experts stay current with evolving requirements from major regulatory bodies worldwide, helping you navigate the specific data needs for your product claims. We provide complete regulatory dossier preparation and submission support, and we stand by your side throughout the review process to defend results if questions arise.
- US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) submission support
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requirements
- Health Canada registration guidance
- Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) compliance
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) testing standards
- Support for both GLP and non-GLP testing requirements
- Assistance with treated article exemption and related claims
Which Labs Offer This Service
Which Labs Offer This Service
Element’s Life Sciences network includes dedicated facilities for both antimicrobial and pharmaceutical testing. Element Eagan is recognised as a premier antimicrobial testing laboratory, while Element Concord is known for its expertise in pharmaceutical testing services. Beyond these key sites, our team operates from Life Sciences hubs across the world, providing global access to our expert capabilities. Find your nearest Life Sciences hub on our Locations Page.
Standards we test to and products we test
- 21 CFR Part 58 (Good Laboratory Practice for Nonclinical Laboratory Studies)
- ASTM E1052 (Efficacy of Antimicrobial Agents Against Viruses in Suspension)
- ASTM E1053 (Efficacy of Virucidal Agents for Inanimate Environmental Surfaces)
- BS EN 14476 (Virucidal Activity in the Medical Area)
- BS EN 14675 (Virucidal Activity in the Veterinary Area)
- BS EN 16777 (Non-Porous Surface Test for Medical Area)
- TM 100/AATCC 100 Modified for Virucidal Efficacy
- ISO 18184 (Determination of Antiviral Activity of Textile Products)
- JIS Z 2801/ISO 21702 Modification (Antiviral Activity and Efficacy)
- USP <63>, EP 2.6.7 (Mycoplasma Tests)
- USP <87> (Biological Reactivity Tests)
- USP 1072 (Disinfection Validation/Qualification)
Disinfectants and sanitizers
- Liquid disinfectants
- Trigger/pump sprays
- Aerosol sprays
- Pre-saturated towelettes
- Electrostatic sprayer applications
- Hard surface disinfectants
- Soft surface disinfectants
- Laundry additives
Treated articles
- Antimicrobial-treated fabrics
- Woven and knitted fabrics
- Fibers, yarns, braids
- Antimicrobial-treated surfaces
- Long-lasting surface coatings
- Copper-containing surfaces
Pharmaceutical products
- Raw materials
- Finished products
- Cell cultures
- Unprocessed bulk samples
- Final filled product samples
Specialty products
- Residual/long-lasting antimicrobial products
- Antimicrobial pesticide devices
- Medical device surface disinfectants
- Topical skin products
- Blood glucose monitoring devices
Your Challenges, Our Solutions
Complex regulations simplified for faster approvals
Defensible efficacy data that strengthens your claims
Customized solutions for your unique products
Accelerated timelines for faster market entry
Why Choose Element

Virucidal testing expertise
Regulatory submission success
Comprehensive virus capabilities
Custom protocol development
30+years
24/7
28


Explore our global network of labs and find your nearest location
VIEW ALL LOCATIONSRelated services
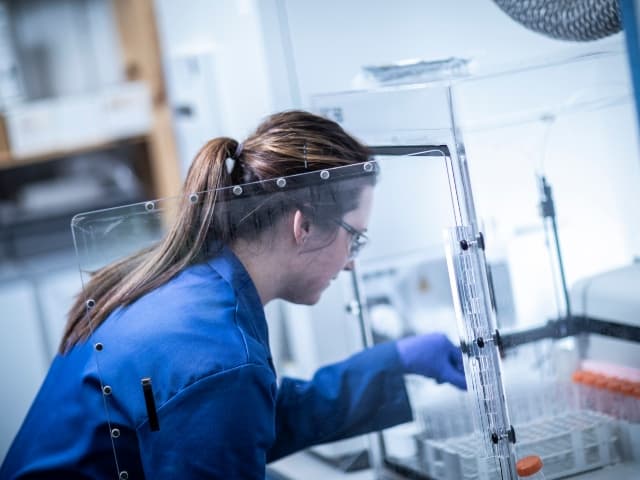

Microbiological Testing and Analysis Services
Element's experts use highly sensitive techniques and the latest analytical methods to provide a wide array of microbiological testing to meet customer specifications and regulatory requirements.
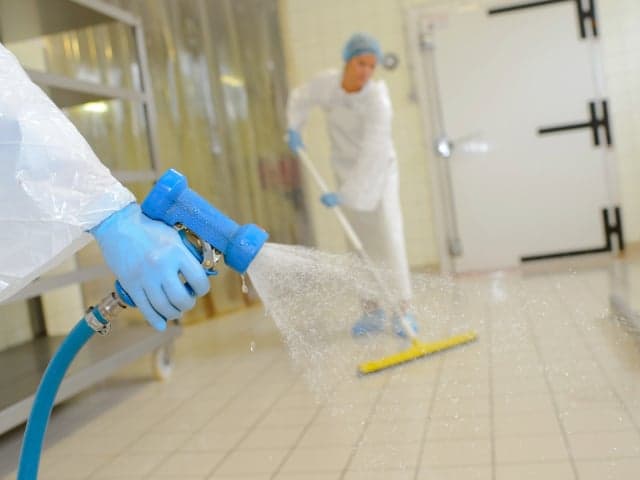

Disinfection Efficacy Testing (DET)
Element's Disinfectant Efficacy Testing provides in-depth microbial elimination analysis in aseptic and controlled environments. Custom protocols and comprehensive testing address facility-specific surfaces and contamination risks with data-driven results.
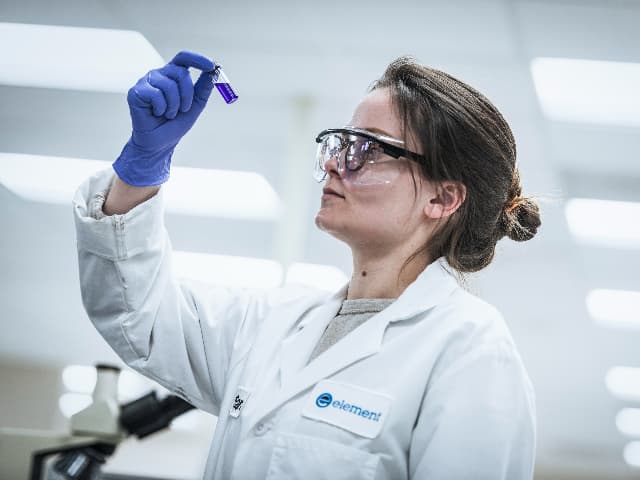

Pharmaceutical Testing Services
Element leads the way in pharmaceutical testing services, delivering trusted expertise from prototype to analysis and finished product. With 150+ global pharmaceutical experts and 30+ years of experience.
Antimicrobial Testing Services
Accelerate antimicrobial product approval with GLP-compliant testing for EPA, FDA, TGA & more. Element delivers trusted efficacy data to meet global regulations & prove effectiveness against emerging pathogens. Learn More.
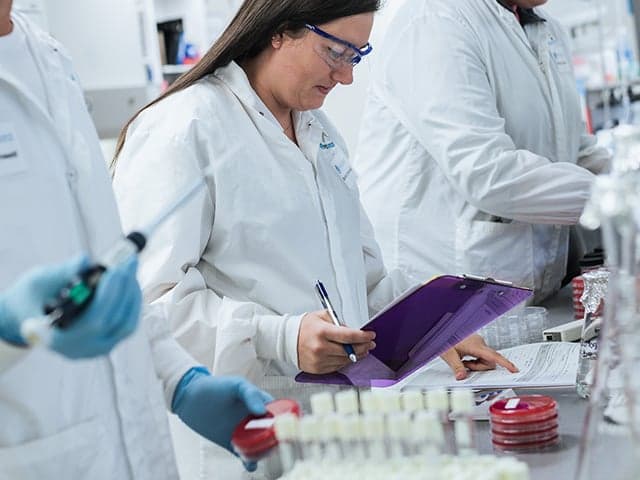

Rapid Sterility and Mycoplasma Solutions
Element provides reliable rapid mycoplasma and sterility testing and delivers results in a matter of days.

Antimicrobial Microbiology Testing Services
Element's knowledgeable microbiologists can test to multiple established methods, as well as developing custom protocols.
