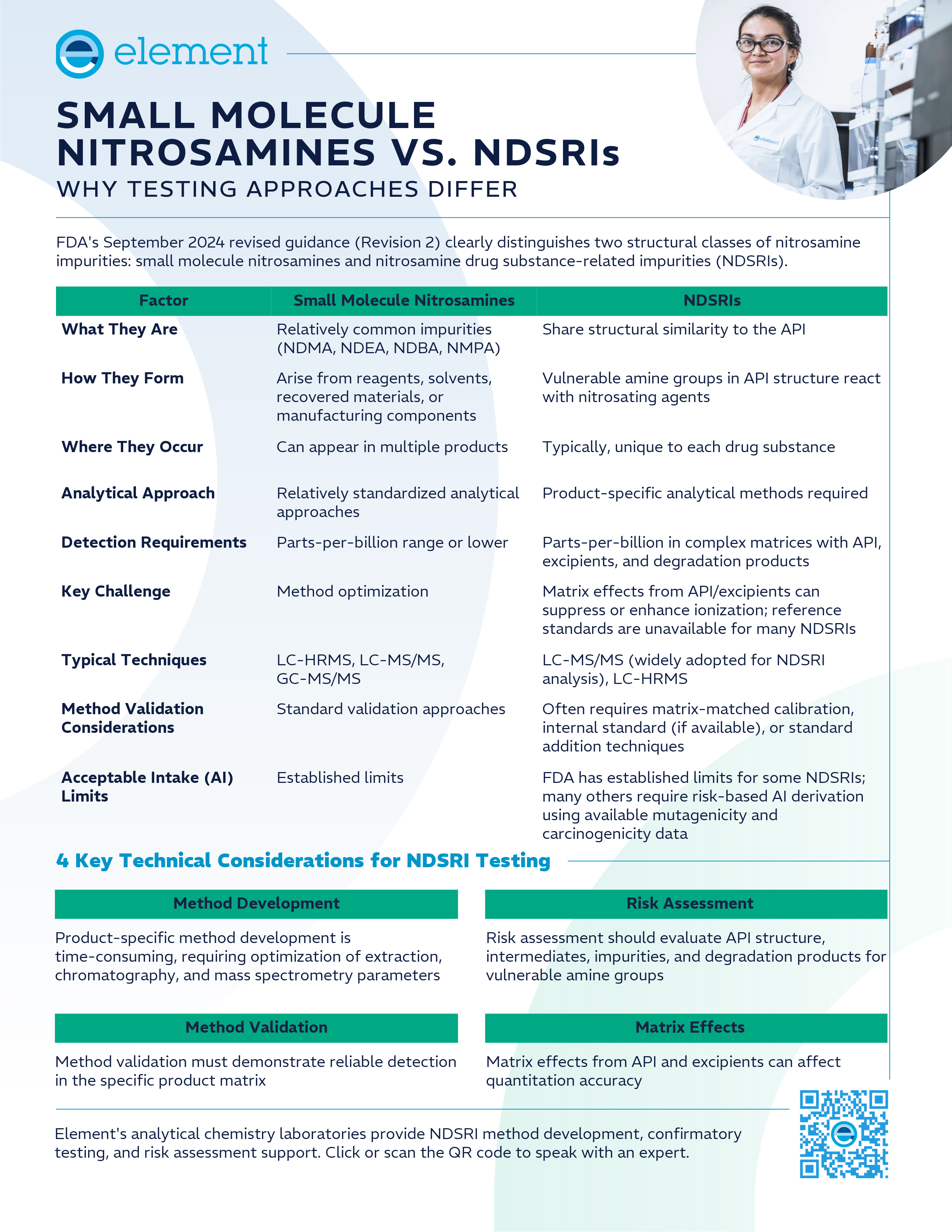
Small Molecule Nitrosamines vs. NDSRIs: Why Testing Approaches Differ
Not all nitrosamine impurities are analytically equivalent. This visual reference clarifies the structural and regulatory distinctions between small molecule nitrosamines and nitrosamine drug substance-related impurities (NDSRIs), and explains why FDA's evolving guidance requires fundamentally different testing strategies for each class.
Understanding Why NDSRI and Small Molecule Nitrosamine Testing Diverge
FDA's September 2024 revised guidance (Revision 2 of "Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Drugs") formalized a distinction that analytical chemists had been navigating in practice for several years: small molecule nitrosamines and nitrosamine drug substance-related impurities (NDSRIs) are structurally and analytically distinct categories that require meaningfully different testing approaches.
For pharmaceutical quality professionals managing nitrosamine control programs, this distinction has direct implications for method development timelines, laboratory selection, and regulatory submission strategy.
The infographic below summarizes the key differences across formation pathways, detection requirements, analytical techniques, method validation considerations, and acceptable intake limit frameworks.
Download a PDF version of this infographic to share with your team or keep as a reference.
4 Key Technical Considerations for NDSRI Testing
The comparison above captures structural and regulatory differences at a glance, but several technical realities deserve additional context for teams building or evaluating NDSRI control programs. These technical requirements - de novo method development, reference standard limitations, and product-specific validation - drive both the extended timelines and resource investments NDSRI programs demand.
- Method Development
Product-specific method development is time-consuming, requiring optimization of extraction, chromatography, and mass spectrometry parameters. Unlike small molecule nitrosamines where established methods often exist and can be adapted with modest optimization, each NDSRI requires methods developed de novo because of its structural uniqueness to the parent API.
- Reference Standards
Reference standards are unavailable for many NDSRIs, which adds meaningful complexity to method development and validation. Without a certified reference standard, laboratories must rely on approaches such as standard addition techniques or matrix-matched calibration to achieve reliable quantitation - requiring additional method development steps before validation can begin.
- Matrix Effects
Matrix effects from API and excipients can affect quantitation accuracy, particularly challenging when detecting parts-per-billion concentrations within matrices dominated by high API concentrations. Managing these effects requires specialized sample preparation protocols and careful method optimization.
- Risk Assessment
Risk assessment should evaluate API structure, intermediates, impurities, and degradation products for vulnerable amine groups. The acceptable intake limit landscape also differs substantially: established AI limits exist for common small molecule nitrosamines like NDMA and NDEA, while many NDSRIs require risk-based acceptable intake (AI) derivation using available mutagenicity and carcinogenicity data.
Using This Infographic for Program Planning
For quality directors and CMC leads explaining NDSRI programs to cross-functional teams, this infographic provides a framework for illustrating where analytical complexity lies. The side-by-side comparison clarifies why product-specific approaches inherently require more time and specialized resources than adapting standardized methods - not inefficiency, but the scientific necessity of developing and validating methods unique to each API structure.
Key Takeaways
- Small molecule nitrosamines allow relatively standardized testing approaches; NDSRIs require product-specific analytical methods
- Reference standards are unavailable for many NDSRIs, adding validation steps not required for small molecule nitrosamines
- Matrix effects from high API concentrations create unique challenges for NDSRI detection at parts-per-billion levels
- Some NDSRIs have FDA-established limits; many require risk-based acceptable intake derivation
- Method development timelines reflect the need to optimize extraction, chromatography, and mass spectrometry parameters for each unique NDSRI structure
- Product-specific method development, reference standard limitations, and matrix effect management drive extended timelines and specialized resource requirements
For a deeper discussion of NDSRI testing requirements, FDA timelines, and what to look for in a testing laboratory partner, see our related article, NDSRI Testing Regulatory Requirements, Challenges and Timelines Explained.
Working with a Testing Laboratory on NDSRI Analysis
The technical complexity outlined above - product-specific method development, reference standard limitations, matrix validation requirements, and risk-based AI derivation - means that laboratory selection matters considerably for NDSRI programs. Facilities with experience across multiple NDSRI projects bring institutional knowledge about which analytical approaches tend to work for different API structural classes, where common method development pitfalls occur, and what regulatory reviewers look for in NDSRI data packages.
Element's analytical chemistry laboratories support pharmaceutical manufacturers across the full scope of nitrosamine control programs, from initial structural risk assessment and confirmatory testing through validated quantitative methods and ongoing monitoring.
Contact our analytical team to discuss your specific program requirements.
Related Services
Extractables and Leachables Testing Services
Element provides tailored extractables and leachables testing (E&L) studies to ensure patient safety and compliance with regulatory requirements.

Stability Testing and Forced Degradation Studies for Pharmaceuticals
ICH-compliant stability storage and testing with integrated analytical services, ensuring controlled conditions from storage through analysis in FDA-registered facilities supporting pharmaceutical development programs.

Analytical Method Development & Validation
Element's regulatory and industry experts have a proven track record of successfully developing and validating fit-for-purpose, accurate, and reliable analytical methods based on established CDER/ICH and FDA guidelines and procedures.
Pharmaceutical Unknown Identification and Impurity Testing
Element offers expert impurity testing services for pharmaceuticals, ensuring drug safety, quality, and compliance with FDA and ICH guidelines through advanced analytical methods and tailored solutions.

Pharmaceutical Testing Services
Element leads the way in pharmaceutical testing services, delivering trusted expertise from prototype to analysis and finished product. With 150+ global pharmaceutical experts and 30+ years of experience.



