How Can Additive Manufacturing Be Safely Implemented for Critical Components? – Element's Innovative Integrity Assurance Methodology
This article outlines Element's collaboration with UKAEA and aerospace partners to develop a risk-based methodology for assessing the safety of additive-manufactured components. By evaluating potential flaws and their impact on fatigue life, the approach enables rapid, geometry-specific risk assessments to inform testing protocols for critical applications in nuclear and aerospace industries.
Background
Additive manufacturing (AM), commonly known as 3D printing, has revolutionized manufacturing by enabling the creation of complex geometries that were previously impossible to produce. Through techniques like selective laser melting (SLM) or direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), metal powders can be fused layer by layer to create components with optimal designs, reduced weight, and enhanced strength. Such components are lighter and stronger than conventional parts, but because of the way they are made the standard methods for assuring their quality cannot be used – which is a particular problem for safety-critical components in high-consequence industries like aerospace and nuclear power.
The challenge
The fundamental challenge was how to reliably validate the structural integrity of additively manufactured components for use in high-risk environments. Unlike conventional manufacturing, where material properties are relatively uniform and predictable, AM processes can produce microscopic anomalies such as voids, inclusions, unfused particles, and anisotropic material properties that vary throughout the component.
These potential defects present unique risks for fatigue life and structural performance, especially under extreme operating conditions.
A new methodology was needed that could:
- Systematically assess the structural integrity risks specific to AM components
- Provide statistical confidence in component performance
- Guide targeted inspection and testing regimes
- Support regulatory approval in highly regulated industries
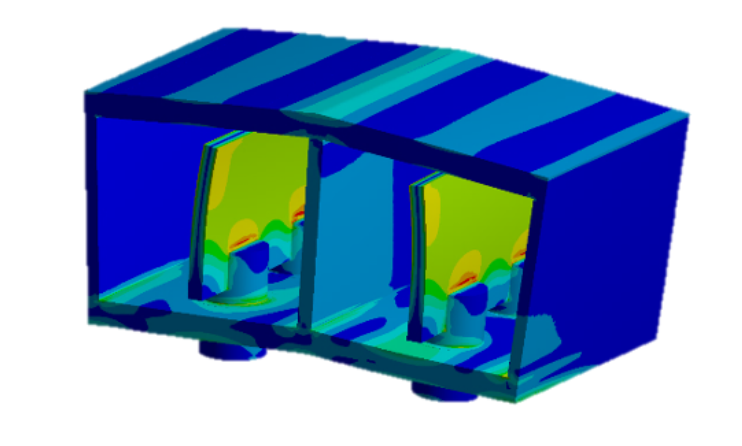
The solution
Working in collaboration with UKAEA, inspection bodies, and aerospace companies, Element’s team of experts developed a risk-based analysis methodology that assessed the fatigue lives for an otherwise perfect component based on a number of worst-case potential flaws then statistically assessed the probability of inclusions, voids, or unfused particles with the critical region. The method was complex but could be automated easily for any given geometry, quickly leading to a risk assessment for that component that would inform the test regime during manufacture.
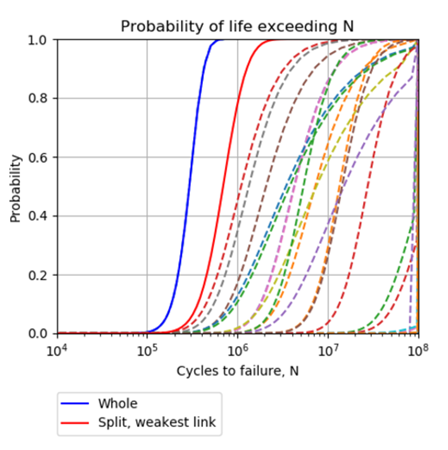
The result
As the field is rapidly expanding, this methodology remains to be further developed to account for the growing range of material types and manufacturing techniques. However, initial test applications of this integrity assurance methodology have been very successful and it provides potential for significant benefits to clients in the aerospace and nuclear sectors.
Related Services

Additive Manufacturing Testing
Element is at the forefront of additive manufacturing technology, providing critical testing services to clients in aerospace, transportation, medical devices, and beyond.

Advanced Modeling and Simulation Services
Elevate your project with Element's modelling and simulation services, including fluid simulation, CFD, FEA, DEM, and electromagnetics. Our industry-leading expertise ensures precision, cost savings and regulatory compliance at every step.

Machine Learning and Data Science Services
Our Machine Learning and Data Science services offer customized solutions to transform your data into actionable insights. We integrate predictive analytics with hardware testing to minimize downtime, optimize resources, and improve safety. Our software-agnostic approach ensures seamless integration with your systems, delivering AI-powered insights tailored to your operational needs.

