Element Engineers Develop New Cast Iron Technology
This article by metallurgical engineers Rick Gundlach and Dr. John Tartaglia introduces a novel heat treatment process for ductile cast iron. By intercritically austenitizing and quenching, they achieve a fine-grained lamellar structure, resulting in improved tensile strength and ductility compared to conventional methods. This advancement offers significant potential for applications requiring high-performance cast iron components.
Building on their earlier work, Element Wixom senior metallurgical engineers Rick Gundlach and Dr. John Tartaglia have conducted innovative research and published scholarly papers about a new heat treatment approach to obtaining superior properties in nodular cast iron.
 Castings of three ductile iron alloys were intercritically (IC) austenitized to produce a fine-grained lamellar austenite-ferrite structure and were subsequently quenched and tempered. After IC austenitizing and quenching, the lamellar austenite grain size was substantially finer than the polygonal austenite grain structure produced by conventional, supercritical austenitizing and hardening above the critical temperature. To maximize strength, the acicular austenite component of the IC heat-treated microstructure should be maximized. Consequently, the casting must be heated as close to the upper critical temperature as possible without losing the fine-grained acicular austenite structure. Since the desired lamellar austenite structure only forms in ferrite, to achieve a uniform acicular structure throughout, it was necessary to eliminate pearlite by ferritizing the material prior to IC heat treatment.
Castings of three ductile iron alloys were intercritically (IC) austenitized to produce a fine-grained lamellar austenite-ferrite structure and were subsequently quenched and tempered. After IC austenitizing and quenching, the lamellar austenite grain size was substantially finer than the polygonal austenite grain structure produced by conventional, supercritical austenitizing and hardening above the critical temperature. To maximize strength, the acicular austenite component of the IC heat-treated microstructure should be maximized. Consequently, the casting must be heated as close to the upper critical temperature as possible without losing the fine-grained acicular austenite structure. Since the desired lamellar austenite structure only forms in ferrite, to achieve a uniform acicular structure throughout, it was necessary to eliminate pearlite by ferritizing the material prior to IC heat treatment.
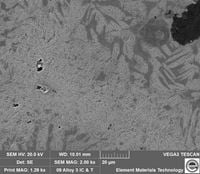
 IC heat treatment produced a unique lamellar structure consisting of acicular martensite in ferrite. The microstructures showed that discrete acicular austenite grains nucleate and grow from the ferrite grain boundaries and result in the formation of a microstructure consisting of “lamellar” austenite in ferrite. After quenching and tempering, the cell boundaries are mostly martensitic, whereas the cell interiors have a mixture of both martensite and ferrite grains with a lamellar grain morphology. The following SEM micrographs show the novel grain structure of martensite and ferrite of this new cast iron.
IC heat treatment produced a unique lamellar structure consisting of acicular martensite in ferrite. The microstructures showed that discrete acicular austenite grains nucleate and grow from the ferrite grain boundaries and result in the formation of a microstructure consisting of “lamellar” austenite in ferrite. After quenching and tempering, the cell boundaries are mostly martensitic, whereas the cell interiors have a mixture of both martensite and ferrite grains with a lamellar grain morphology. The following SEM micrographs show the novel grain structure of martensite and ferrite of this new cast iron.
This novel approach to austenite grain refinement was applied to quench and temper (Q&T) ductile iron in order to improve its tensile properties. When the properties are compared to the standard Q&T grades of ASTM A536 Grade 120-90-02 and ISO 1083 Grade 900-2, the intercritically austenitized alloys exhibited the specified tensile properties with higher ductility. The IC heat-treated grades had up to 5% tensile elongation, which was higher than the standard grades with 2% elongation.
Read more about the investigation and the analysis performed by downloading the article below, or contact us to find out more about chemical analysis, mechanical testing, and microstructural analysis.
Download
Attributes of Q&T Ductile Iron with Novel Microstructures Copyright 2022 American Foundry Society. Originally appearing in the International Journal of Metalcasting, Vol. 17, Issue 2 and made available as an electronic reprint with the permission of the American Foundry Society.
Related Services

Metallurgical Testing Services
Expert metallurgical testing services to verify material integrity and prevent failures. Our accredited laboratories deliver precise analysis of metal microstructures, properties, and defects with expedited options. Ensure product reliability and compliance with industry standards.

On-Site Metallographic Testing and Analysis
Element's on-site metallographic testing provides non-destructive analysis to assess material condition, detect defects early, and support informed decision-making in aerospace, oil & gas, and industrial applications.

Powder Characterization Services
Element's powder characterization services support additive manufacturing by verifying material properties, batch consistency, and compliance with industry standards for optimal performance in 3D printing applications.




